|
|
Vasquez Rocks County Park
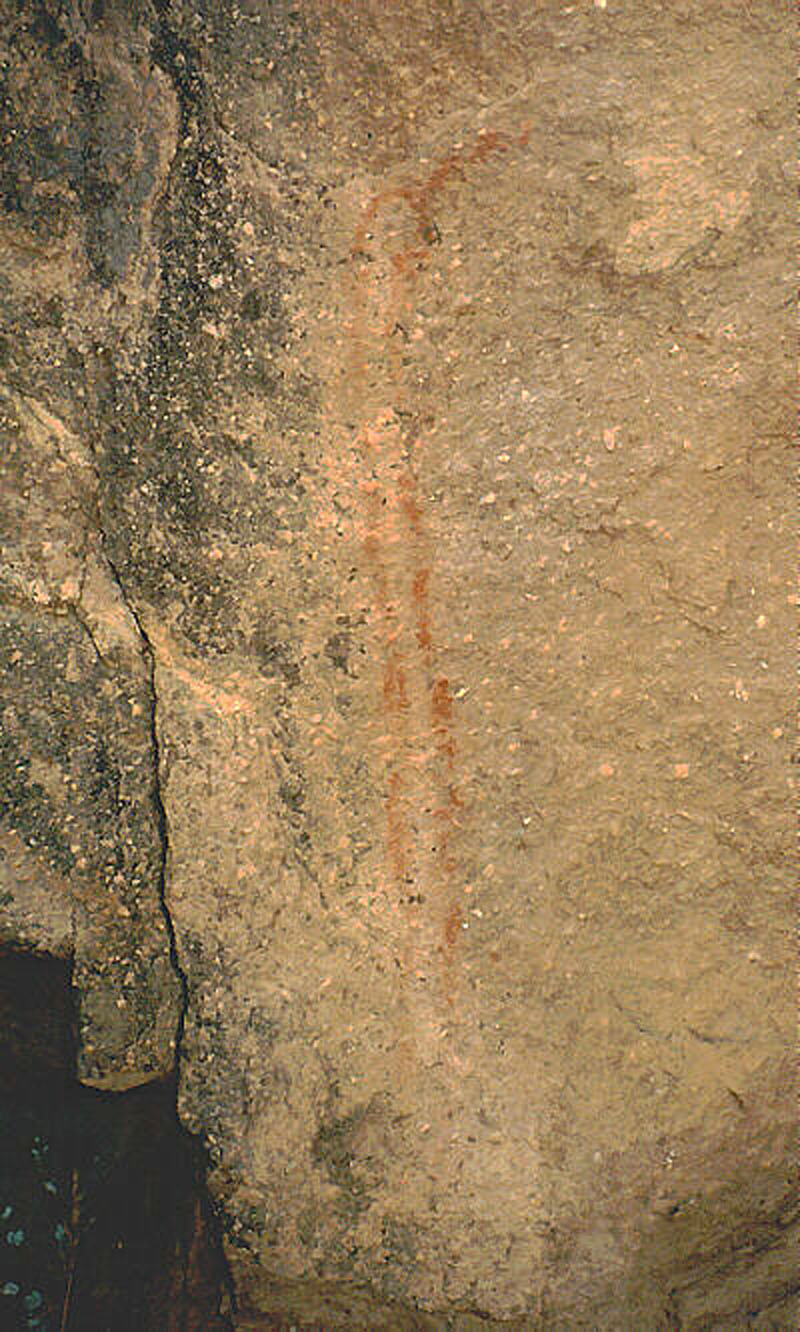

A painting of a snake, in red, at the entrance to a cave at Vasquez Rocks. You can't get more symbolic than that. Most rock art was created by shamans, who were usually men, at the place where they entered the supernatural world. From other pictographs at this site, we know Vasquez Rocks was one such location. When the shaman exited his trance — induced by sensory deprivation, physical stress and a hallucigen, usually native tobacco and more rarely the dangerous jimsonweed — he would depict something he saw in a vision. In the case of pictographs, shamans painted in black (charcoal), red (either from hematite or a certain pond algae) and/or white (kaolin clay). The rattlesnake was a guardian of the supernatural world. But that doesn't necessarily mean this snake was painted by a shaman. If we apply the findings of archaeologist and rock art expert David S. Whitley, Ph.D., to this site, we can suppose that because the snake is red, it might have been painted by a female. Red, the color of menstruation, was the "girls'" color, while boys painted in black. Both particpated in puberty rituals. The girls' rites were more intense. They learned the ways of adult life and childbirth in a ritual which, like that of the shaman himself, involved sensory deprivation, fasting and the injestion of tobacco to induce a hallucination. The girl, now a young woman, would emerge from the experience and, at the shaman's special supernatural place, depict something she saw in a vision. Not only was the rattlesnake the guardian of the supernatural world; it was also the mythical guardian of the vagina. "There is an obvious physical analogy between the caves and rock shelters of many rock art sites" — such as the cave next to this snake painting — "and vaginas/wombs," Whitley writes (1996:24-25). "The shaman's entry through this portal to the sacred realm was thus a kind of ritual intercourse with his rock art site, a metaphorical vagina." Girls' puberty rites were not considered successful unless a supernatural snake that lived in a cave "appeared at the ceremony and showed itself to the girls during their visions, thus becoming their spirit helper" (Whitley 1996:26). Zig-zag and diamond-chain patterns are the dominant forms used by girls throughout the Far West to depict rattlesnakes, Whitley writes, but other forms are also known. We have no knowledge of the date of the art at Vasquez Rocks. Rock art in the Far West probably first appeared with the arrival of the first people and continued well after European contact. Realistically, any painting that's older than a century or two and is exposed to the elements, not in a cave, probably would have faded or worn away.
The Tataviam Indians, a Shoshone-speaking people, arrived in the Upper Santa Clara River Valley (Santa Clarita Valley) about AD 450. They occupied an area bounded by Piru to the west, Newhall to the south, the Liebre Mountains to the north, and Soledad Pass to the east. The word tataviam roughly translates into "People of the Sunny Slopes." Their Chumash neighbors on the coast called them "Aliklik," believed to be a derogatory term mimicking the clicking sound of their language. While it is not known exactly who preceded the Tataviam, the same area was occupied by a people, probably of Chumash origin, who arrived somewhere between 4,000 and 10,000 years ago. The Tataviam were hunter-gatherers who organized into a series of autonomous tribelets throughout the region. They ate acorns, yucca, juniper berries, sage seeds and islay, and they hunted small game. They likely practiced a shamanist religion that put them in touch with the supernatural world through trances and hallucinations brought on by the ingestion of jimsonweed, native tobacco and other psychoto-mimetic plants found along the local rivers and streams. Such habitats also provided raw materials for baskets, cordage and netting. The arrival of Spanish settlers in 1769 led to the demise of the Tataviam people. The Spanish rounded up the aborigines in the early 1800s and conscripted them for manual labor at the mission ranches and vineyards, where they intermarried with other native folk from other parts of Southern California. Juan José Fustero, who may have been the last local full-blooded indigenous person (his father was Tataviam, his mother Tataviam and Kitanemuk) died June 30, 1921, at Rancho Camulos, near Piru.* The Tataviam left behind a vast treasure of rock art at Vasquez Rocks, which is thought to have been a major trading crossroads. The Indians used berries, charcoal and other indigenous materials to emblazon a variety of images inside caves and onto the rock surfaces. Most images had religious meanings, and while they suffered both natural degredation and vandalism during the 20th Century, steps have been taken to preserve them. The most significant 40-acre region was closed to the public in 1996. * NOTE: While Fustero liked to bill himself as the "Last of the Piru Indians," an article in the Los Angeles Herald Examiner in 1965 says that Fustero may actually been married to a full-blooded Tataviam woman, and that they had children. According to the tribes that represent local Native American families, as of 1997 there were approximately 600 persons of Tataviam descent living in Los Angeles County. Update: The pictographs have been off-limits to the public since 1996. Photograph by Leon Worden in 1995. Further reading: The Tataviam: Early Newhall Residents by Paul Higgins.
|
Bowers Cave Specimens (Mult.)
Bowers on Bowers Cave 1885
Stephen Bowers Bio
Bowers Cave: Perforated Stones (Henshaw 1887)
Bowers Cave: Van Valkenburgh 1952
• Bowers Cave Inventory (Elsasser & Heizer 1963)
Tony Newhall 1984
• Chiquita Landfill Expansion DEIR 2014: Bowers Cave Discussion
Vasquez Rock Art x8
Ethnobotany of Vasquez, Placerita (Brewer 2014)
Bowl x5
Basketry Fragment
Blum Ranch (Mult.)
Little Rock Creek
Grinding Stone, Chaguayanga
Fish Canyon Bedrock Mortars & Cupules x3
2 Steatite Bowls, Hydraulic Research 1968
Steatite Cup, 1970 Elderberry Canyon Dig x5
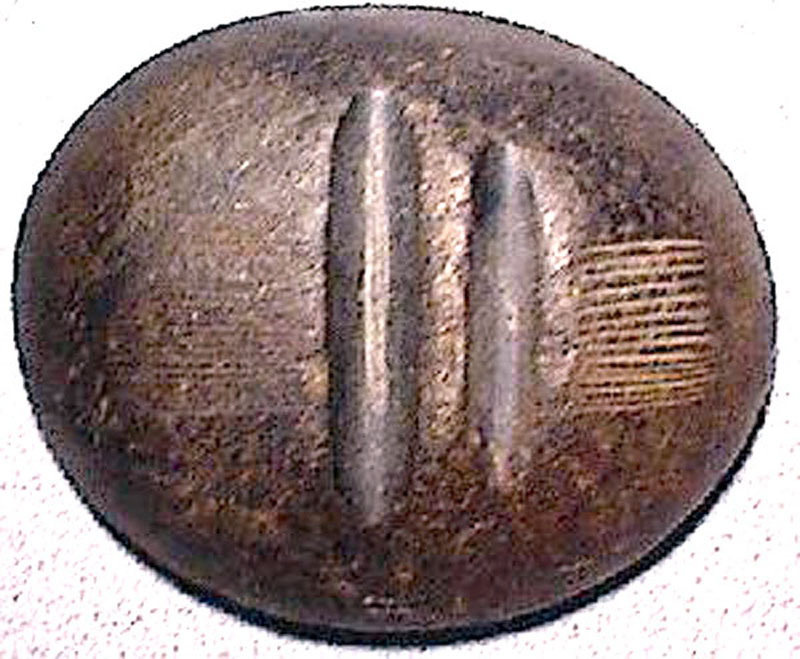
Ceremonial Bar, 1970 Elderberry Canyon Dig x4
Projectile Points (4), 1970 Elderberry Canyon Dig
Paradise Ranch Earth Oven
Twined Water Bottle x14
Twined Basketry Fragment
Grinding Stones, Camulos
Arrow Straightener
Pestle
Basketry x2
Coiled Basket 1875
Riverpark, aka River Village (Mult.)
Riverpark Artifact Conveyance
Tesoro (San Francisquito) Bedrock Mortar
Mojave Desert: Burham Canyon Pictographs
Leona Valley Site (Disturbed 2001)
2 Baskets
So. Cal. Basket
Biface, Haskell Canyon
2 Mortars, 2 Pestles, Bouquet Canyon
|
The site owner makes no assertions as to ownership of any original copyrights to digitized images. However, these images are intended for Personal or Research use only. Any other kind of use, including but not limited to commercial or scholarly publication in any medium or format, public exhibition, or use online or in a web site, may be subject to additional restrictions including but not limited to the copyrights held by parties other than the site owner. USERS ARE SOLELY RESPONSIBLE for determining the existence of such rights and for obtaining any permissions and/or paying associated fees necessary for the proposed use.